How Marvelmind Indoor Positioning System Works
Marvelmind is a full-stack indoor positioning and navigation system for robots, AGVs, drones, forklifts and people. It combines ultrasound Time-of-Flight ranging, synchronized timing, and advanced filtering into a complete, industrial-grade indoor “GPS”.
This page explains how the system works internally: which components are involved, how distances are measured, how maps and submaps are organized, and how the system maintains stable centimeter-level accuracy in real-world industrial environments.
Request Technical Consultation ↗
Talk directly with Marvelmind engineers about your robots, AGVs, drones, forklifts, or people-tracking project.
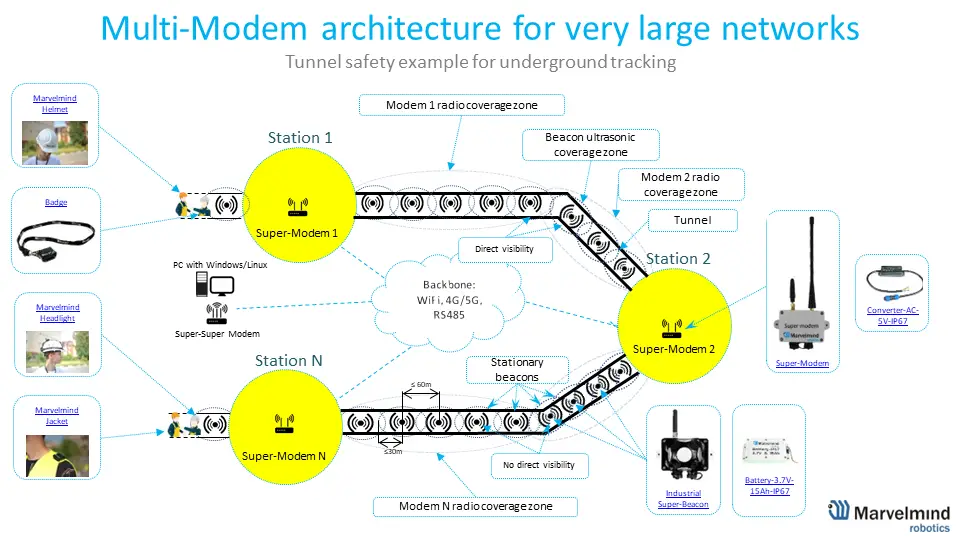
High-level Marvelmind IPS architecture: stationary and mobile beacons, modem and software. For a deeper technical overview, see architectures comparison (PDF) and navigation system manual (PDF).
1. System Overview: A Complete Indoor Navigation Stack
Marvelmind is not just a sensor; it is a complete indoor navigation stack designed for industrial robotics. The system combines:
- Ultrasound-based distance measurement between mobile and stationary beacons
- A synchronized RF timing network controlled by the modem
- Map and submap logic for large, multi-floor facilities
- IMU fusion and filtering for smooth trajectories (optional)
- Rich integration APIs for robots and automation systems
A high-level introduction to indoor positioning principles is given in How Indoor Positioning Systems Work. Marvelmind applies these principles in a robust, field-proven way focused on industrial accuracy and reliability.
For a concise comparison of Marvelmind versus other technologies, see Why Marvelmind.
2. Main Components and Their Roles
Marvelmind IPS consists of four key building blocks:
- Mobile beacons – installed on robots, AGVs, drones, forklifts or people
- Stationary beacons – fixed reference points in the environment
- Modem / Super-Modem – central timing and data hub
- Dashboard software – configuration, monitoring and visualization
Mobile beacons emit or receive ultrasound, stationary beacons provide the fixed acoustic reference, the modem synchronizes and collects data, and Dashboard visualizes and manages the system.
The full component set and example architectures are described in Marvelmind presentation (PDF).
3. Ultrasound Time-of-Flight and Ranging Modes
Marvelmind uses ultrasound Time-of-Flight (ToF) as the primary way to measure distances. The core idea is simple: measure how long it takes for an ultrasound pulse to travel between beacons. Because sound travels relatively slowly (≈340 m/s), the system can resolve distance with centimeter-level precision.
The system supports several ranging modes:
- One-way ranging (OWR) – mobile beacons emit ultrasound, stationary beacons receive and timestamp it. This is the most basic architecture for robots, drones, and AGVs – Non-Inverse Architecture (NIA).
- Reverse one-way – stationary beacons emit, mobile beacons receive. Useful wearable scenarios (people tracking), forklifts, and robots – Inverse Architecture (IA).
- Hybrid modes – used for diagnostics or special layouts where both directions are beneficial – the mode when the map of stationary beacons is being build automatically.
How ultrasound compares to other technologies (such as UWB) in terms of ranging, noise and multipath is covered in Why Ultrasound is More Accurate than UWB and UWB Positioning vs. Ultrasound.
4. Synchronized Timing: The Invisible Backbone
To compute positions, the system must know not only when ultrasound pulses arrive, but also how clocks of all beacons relate to each other. Marvelmind uses a synchronized RF timing network controlled by the modem.
The modem broadcasts timing frames over radio. Stationary beacons lock their internal clocks to those frames, so the entire system operates on a shared time base. When a stationary beacon detects ultrasound, it records the arrival time and sends the timestamp to the modem.
With multiple timestamps from different stationary beacons, the system solves for the position of the mobile beacon via trilateration in 2D or 3D. The tight synchronization of clocks is what makes centimeter-level accuracy possible over long periods of time.
5. Sensor Fusion and Smooth Trajectories
Raw ultrasound ranges provide very accurate but discrete position fixes. To obtain smooth, continuous trajectories, Marvelmind fuses ultrasound with IMU data (accelerometers and gyroscopes) available on mobile beacons (optional) or other sources of data, for example, odometry.
When ultrasound is briefly blocked, the IMU + odometry performs dead reckoning and propagates position. When ultrasound measurements become available again, they correct accumulated drift. This combination provides:
- Smoother movement for visualization and logging
- Better behavior for fast-moving robots and drones
- Robustness against short-term occlusions and acoustic shadows
The internal filtering algorithms are described at a high level in the Marvelmind presentation and user documentation.
6. Maps, Submaps and Large Facilities
Real factories and warehouses are rarely a single simple room. Marvelmind supports dividing the installation into submaps: logical areas with their own sets of stationary beacons and configuration.
Submaps can represent different halls, zones, or floors. The modem and Dashboard align them into a single global coordinate system. A robot can move from one submap to another without losing its position.
Typical deployments include:
- Multi-hall warehouses
- Production lines with separate acoustic zones
- Multi-level logistics centers
The principles of designing such systems are discussed in the navigation system manual and related engineering guides.
7. APIs, Integration and Practical Robotics Use
Marvelmind is designed to be integrated directly into robotics, automation and digitalization projects. It exposes positions and diagnostics via multiple interfaces:
- ROS / ROS2 – for integration with robot operating systems
- UART – binary protocol for embedded controllers
- USB – for PCs and industrial computers
- SPI and NMEA – for systems that expect GNSS-like messages
- RS-485 – for truly industrial environment
- UDP over WiFi – when wireless streaming of data is preferred
Links to protocol documents, examples and integration guides are collected on the Download page and in the Marvelmind Interfaces PDF.
Combined with high accuracy, robust behavior in metal-rich environments and flexible deployment architectures, this makes Marvelmind a practical foundation for indoor navigation of robots, AGVs, drones and industrial vehicles.
8. Conclusion: A Field-Proven Indoor Navigation System
Marvelmind Indoor Positioning System combines ultrasound Time-of-Flight, synchronized timing, submap architecture and rich APIs into a mature, field-proven navigation solution.
- Centimeter-level accuracy in real industrial conditions
- Stable operation in metal-rich and RF-noisy environments
- Scalable from small test labs to large factories
- Direct integration with robots, AGVs, drones, forklifts and people-tracking systems
If you need precise and robust indoor navigation for your autonomous system, Marvelmind provides a complete and well-documented architecture with many reference deployments worldwide.
Ready to talk about your use case? Request Technical Consultation.